Cloud
What is cloud computing
Learn what cloud computing is, how it works, and why businesses use cloud hosting for flexibility, scalability and cost-efficient infrastructure.
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing resources—such as servers, storage and applications—over the internet instead of running them on physical hardware you manage. It offers on-demand scalability, predictable performance and flexible pricing, making it suitable for a wide range of business environments and technical requirements.
Simply put, cloud computing means accessing and storing data and applications over the internet instead of on your computer’s hard drive or local servers. It’s like electricity: you don’t generate power yourself; you simply plug into the grid and pay for what you use.
The basics of cloud computing
Cloud computing represents a shift in how IT resources are delivered. Instead of buying, installing and maintaining hardware and software, users access these as services hosted in remote data centres managed by providers like xneelo. Through an internet connection, you get the same functionality you’d have with on-premises infrastructure but without the upfront costs and complexity.
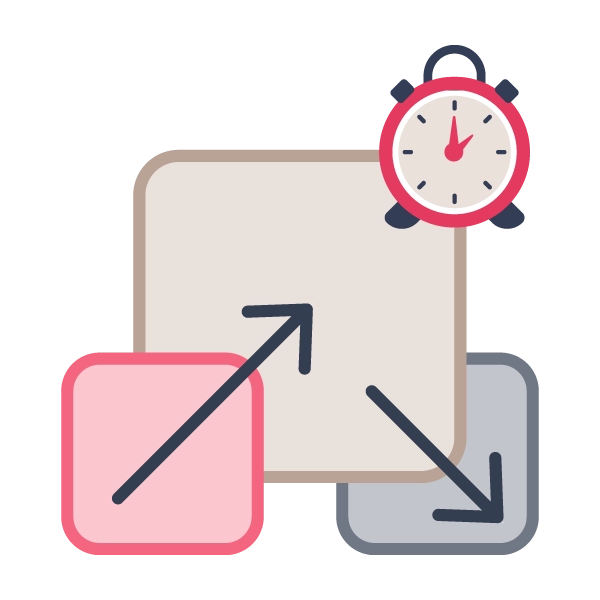

On-demand availability
Scale resources up or down as needed
Pay-as-you-go pricing
Billed based on actual consumption, like utilities
Accessibility
Use services anywhere with internet access
Core cloud computing service models
Cloud computing services typically fall into three primary models, each suited to different business needs and technical requirements.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service provides virtualised computing resources over the internet. This includes virtual machines, storage, networks and operating systems. With IaaS, businesses can rent IT infrastructure on a pay-as-you-go basis instead of purchasing physical servers.
Common IaaS examples include virtual private servers, backup services and disaster recovery solutions. This model is particularly valuable for businesses that need computing resources but want to avoid the capital expense and complexity of managing physical hardware.

Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service offers a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud. PaaS provides the infrastructure plus middleware, development tools, database management systems and business intelligence services.
This model enables developers to build, test, deploy and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. Popular PaaS offerings include web application hosting platforms and database services that automatically handle scaling and maintenance.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service delivers fully functional applications over the internet. Users access these applications through web browsers without needing to install or maintain software locally.
Common SaaS examples include email services, customer relationship management systems and collaboration tools. This model offers the greatest simplicity for end users, as the service provider handles all technical aspects, including updates, security and maintenance.
Cloud deployment models explained
Understanding different deployment models helps businesses choose the right cloud strategy for their specific needs and requirements.

Public cloud computing
Public cloud services are owned and operated by cloud service providers and delivered over the internet. These services are available to anyone who wants to purchase them, offering the greatest cost efficiency and scalability.
Public clouds work well for businesses with variable workloads, those seeking to minimise IT costs or organisations that need to scale quickly. The shared infrastructure model allows providers to offer services at lower costs while maintaining high performance and reliability.
Private cloud computing
Private cloud computing refers to cloud resources used exclusively by one organisation. Private clouds can be physically located at the organisation’s data centre or hosted by a third-party provider.
This model offers greater control over security, compliance and customisation. Private clouds are often chosen by organisations with strict regulatory requirements or those handling sensitive data that requires enhanced security measures. Private cloud can be more costly than public cloud due to dedicated infrastructure, but it delivers unmatched control and compliance assurance.

Hybrid cloud computing
Hybrid cloud computing combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to move between environments as computing needs and costs change.
This approach provides greater flexibility and optimisation opportunities. Businesses can keep sensitive data in private clouds whilst leveraging public cloud resources for less critical workloads or to handle traffic spikes
Benefits of cloud computing
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages that have driven its widespread adoption across industries and organisation sizes.

Cost efficiency and predictable expenses
One key advantage of cloud computing is the transition from capital expenses to operational expenses. Businesses only pay for cloud services as needed, which reduces the risk of over- or under-provisioning resources. This model also eliminates costs related to maintaining and upgrading physical infrastructure.
Scalability and flexibility
Cloud computing provides scalability, enabling businesses to adjust resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during peak times and cost savings during slower periods. It also allows services to be deployed closer to customers, enhancing performance and offering global accessibility previously available only to larger companies with significant IT budgets.

Enhanced security and reliability
Cloud providers prioritise robust security measures, including physical security, network security, data encryption and regular audits, surpassing what many organisations can implement. Their service level agreements also guarantee uptime levels that are challenging for on-premises infrastructure to match.
Automatic updates and maintenance
Cloud services offer automatic updates, security patches and system maintenance, easing the load on IT teams and keeping systems secure. These updates allow businesses to enjoy the latest features and improvements without disrupting operations.
Real-world cloud computing applications
Cloud computing powers many services that have become integral to daily business operations and personal activities.
Business applications
Modern businesses rely on cloud-based email systems, file sharing platforms and collaboration tools. Customer relationship management systems, accounting software and project management tools are increasingly delivered as cloud services.
E-commerce platforms use cloud computing to handle traffic loads that vary, process payments securely and manage inventory across multiple channels. The scalability of cloud services means these platforms can accommodate everything from small online shops to global marketplaces.
Development and innovation
Software development teams use cloud platforms to build, test and deploy applications more efficiently. Cloud-based development environments enable collaboration across geographical boundaries and provide access to powerful computing resources when needed.
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning and data analytics are increasingly offered as cloud services, providing advanced capabilities to businesses that previously could not afford the necessary infrastructure.
Data storage and backup
Cloud solutions provide secure and resilient storage for your data to reduce the risk of data loss due to hardware failures. The information stored in the cloud is accessible whenever and wherever you need it, making it a reliable platform for your operations.
Businesses can use cloud storage as part of their own backup or disaster recovery strategies, though configuring and managing backups remains the responsibility of the customer.
Choosing the right cloud computing solution
Selecting the right cloud services requires careful consideration of business requirements, technical needs and organisational constraints.
Xneelo Cloud: Simple, flexible cloud for South African businesses
Xneelo Cloud offers reliable, high-performance infrastructure with built-in redundancy to ensure secure and resilient resources. While you handle your own backups and applications, our platform supports your disaster recovery strategies. With global-standard infrastructure and local compliance (including POPIA), xneelo Cloud simplifies getting started, scaling quickly and maintaining control over your environment.
- 100% South African cloud, with local pricing, support and infrastructure
- Easy cloud management with a user-friendly dashboard
- Simple and transparent pay-as-you-go pricing without long-term contracts