How to deal with phishing scams
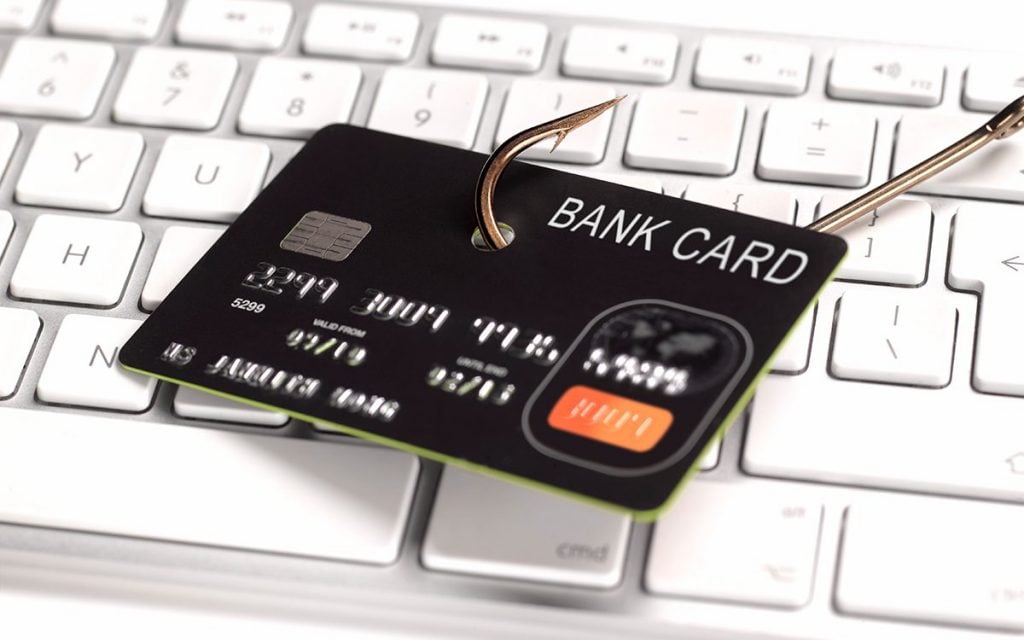
Phishing is a fraudulent attempt to obtain sensitive information such as usernames, passwords and credit card details. This is usually done by disguising as a legitimate, trustworthy entity on websites, by email, SMS or even telephonically.
If you’ve encountered spam, phishing, fraud, or any other misuse from our network, use this form to report it.
Example scenarios
- You receive a phishing email asking for sensitive information and you are instructed to reply to the email providing the requested information.
- You receive a phishing email instructing you to click a link where you are taken to a website that looks like the legitimate website of the company you think you are dealing with. You then enter sensitive information such as your username and password on the fake page.
- You receive a phone call from someone posing as a member of an organisation such as your bank. They gain your trust by knowing some of your information, such as name, address and ID number and so you inadvertently provide them with further information such as a login or password.
- You receive an email with an attachment. When you open the attachment, your PC gets infected with a virus (malware) that harvests your usernames and passwords.
How to prevent becoming a victim
- Delete email and text messages that ask you to confirm or provide personal information. Legitimate companies don’t ask for this information via email or text. The messages may appear to be from organizations you do business with and may threaten to close your account or take other action if you don’t respond. Don’t reply, and don’t click on links or call phone numbers provided in the message. These messages direct you to spoof sites that look real but whose purpose is to steal your information so a scammer can run up bills or commit crimes in your name.
- Don’t click on links to access login pages unless you are sure they are legitimate. Just like banks and other secure institutions, we won’t ask you to sign in via a link on an email, but will rather give you the full URL e.g. https://create.xneelo.com
- Use trusted security solutions to protect your computer and store your passwords.
- Don’t email personal or financial information. Email is not a secure method of transmitting personal information. Hacked mailboxes are a common method of gathering this information.
- Review credit card and bank account statement as soon as you receive them to check for unauthorized charges.
- Be cautious about opening attachments and downloading files from emails. These files may contain viruses or other malware that can weaken your computer’s security.
Read more about what you need to know about phishing scams