1. Delete unnecessary users and reset password(s)
- Log in to the Remote Control
- If a Runtime error notification pops up, press Cancel
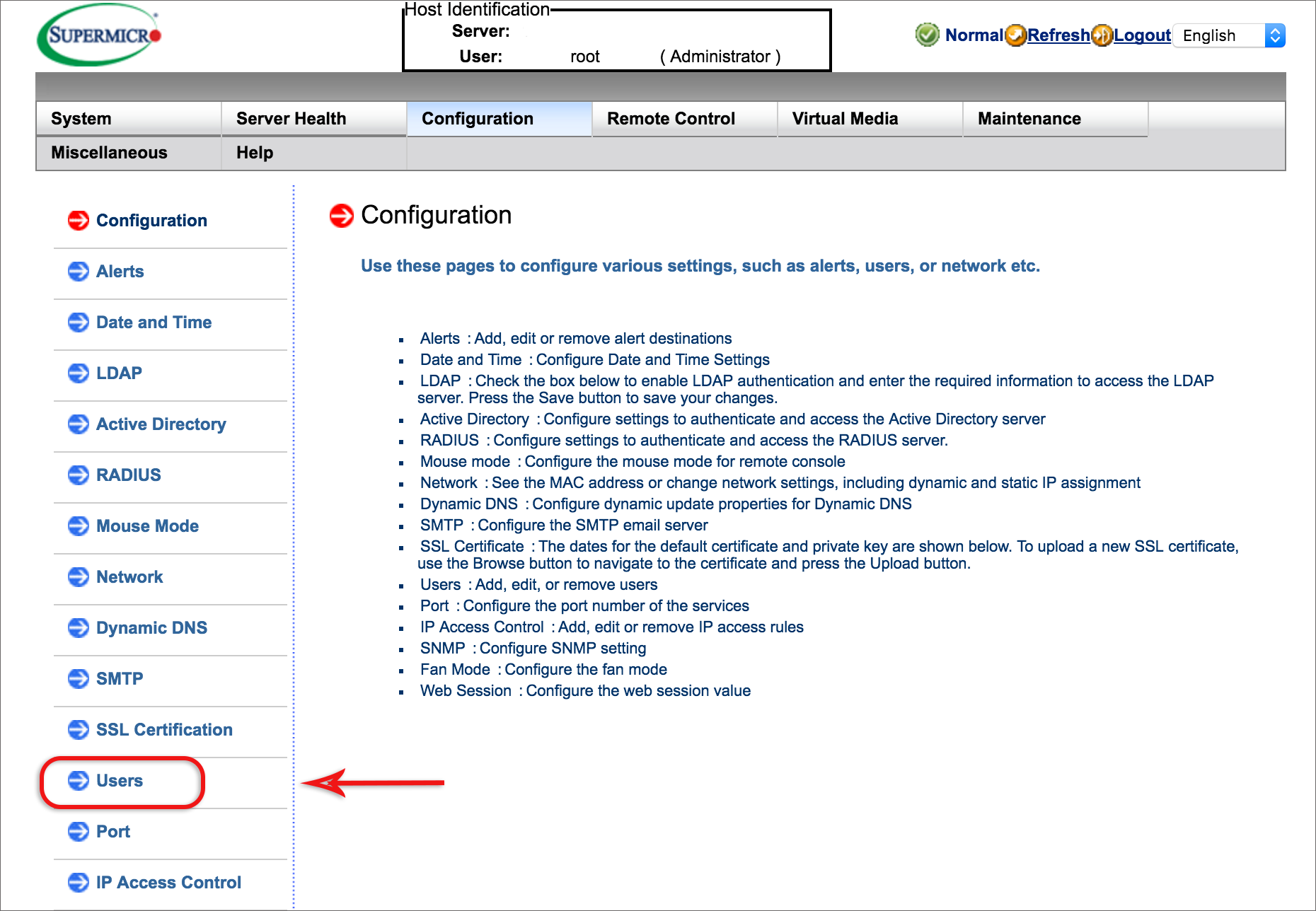
- Select the Configuration tab from the top menu

- Select Users from the left side menu

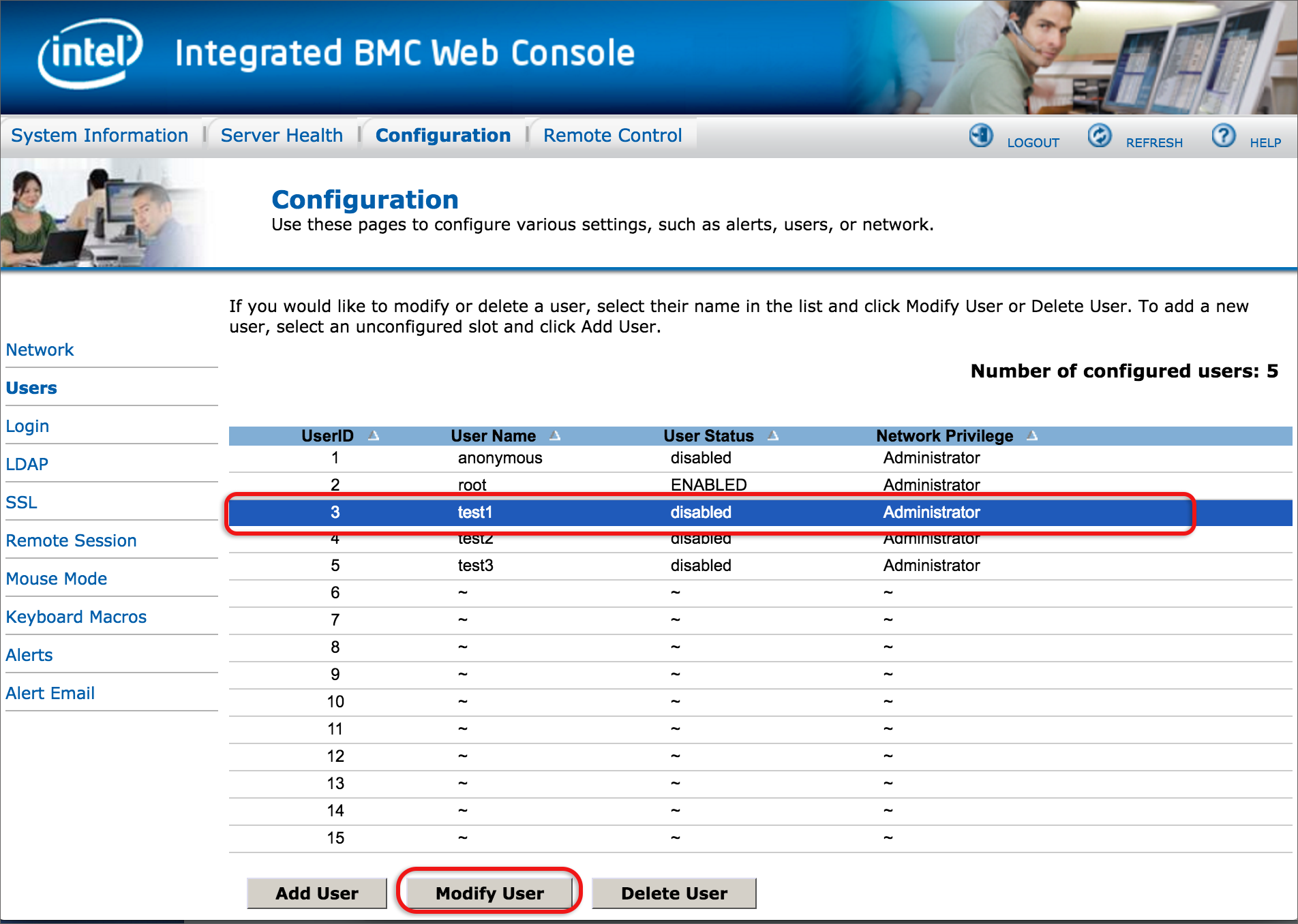
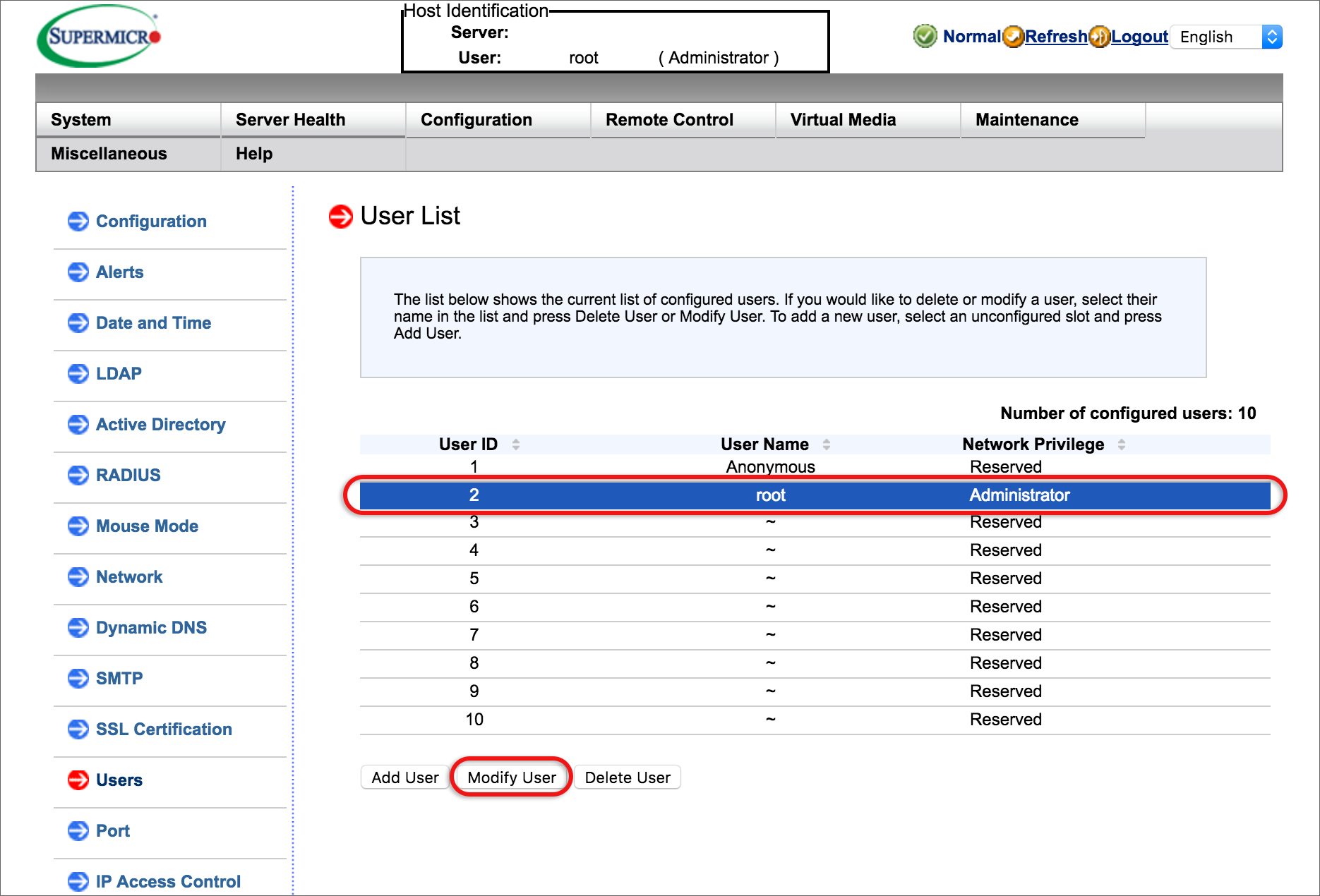
- Delete all users that are not required by selecting the UserID and then clicking the Delete User button. Only the root user can’t be deleted and may be the only one required.
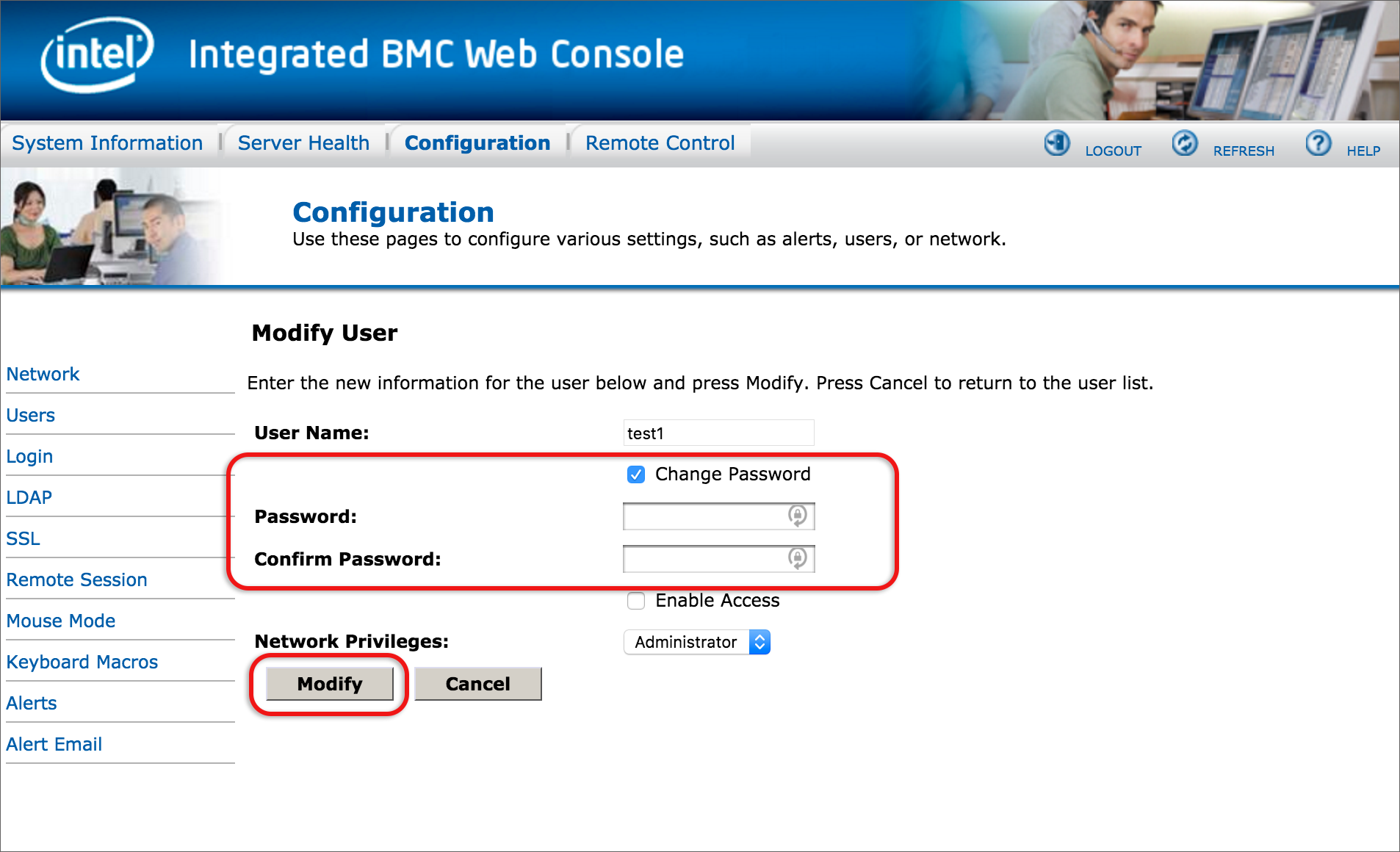
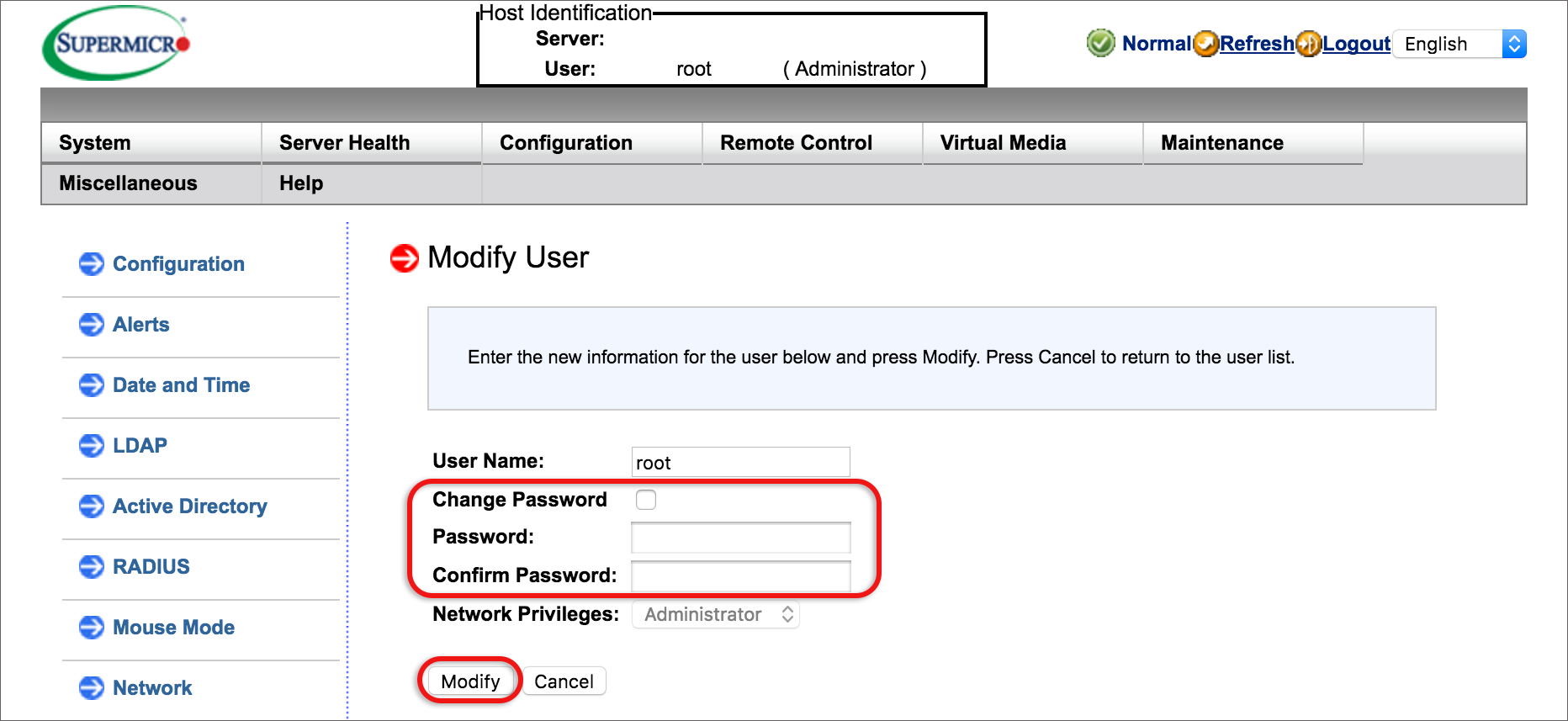
- Update the user(s) passwords: select the relevant user, then click Modify User.

- Ensure that Change Password is ticked and then specify a new password of up to 19 characters.
- Select the Modify button at the bottom of the page.

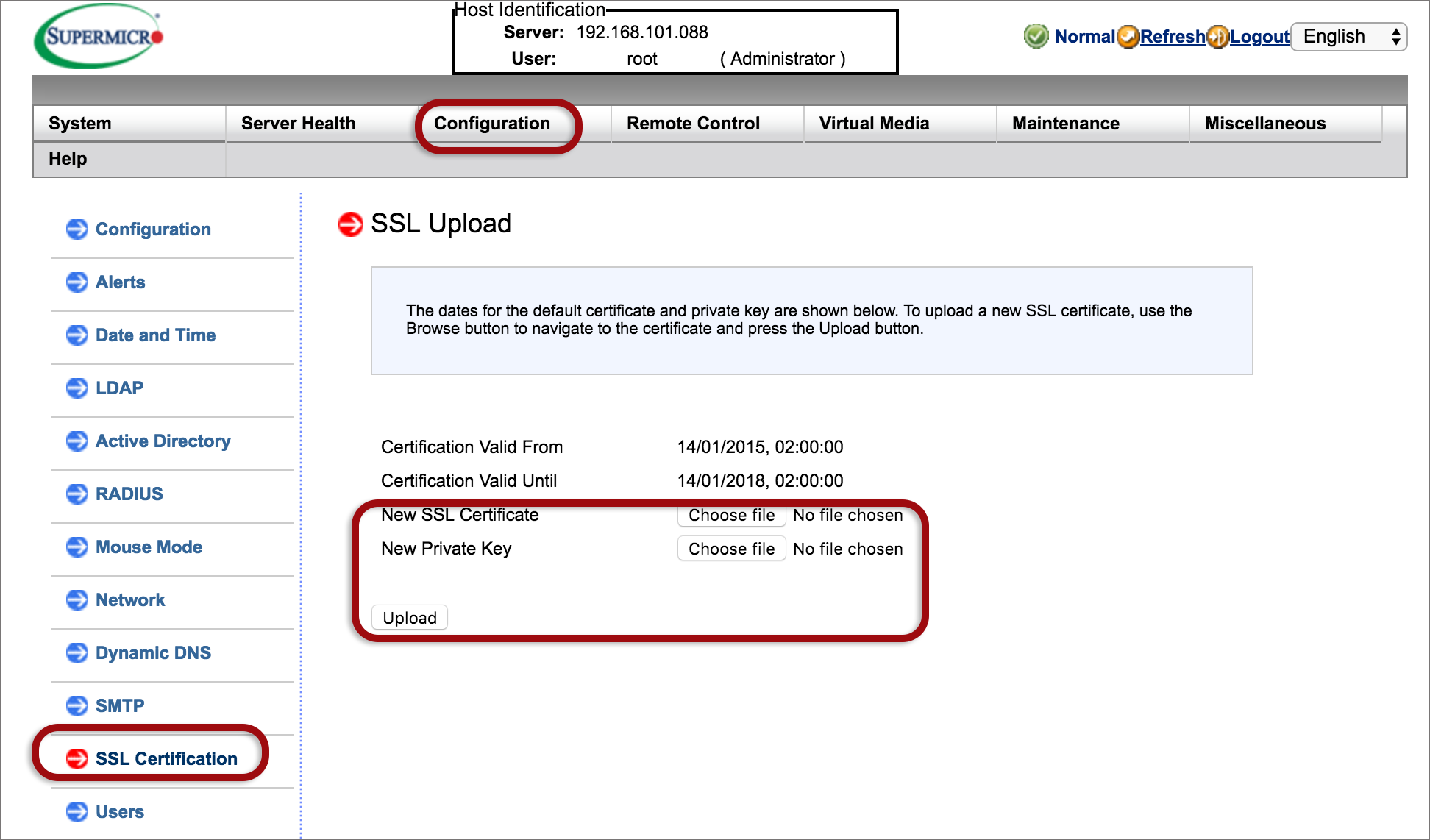
2. Install an SSL certificate
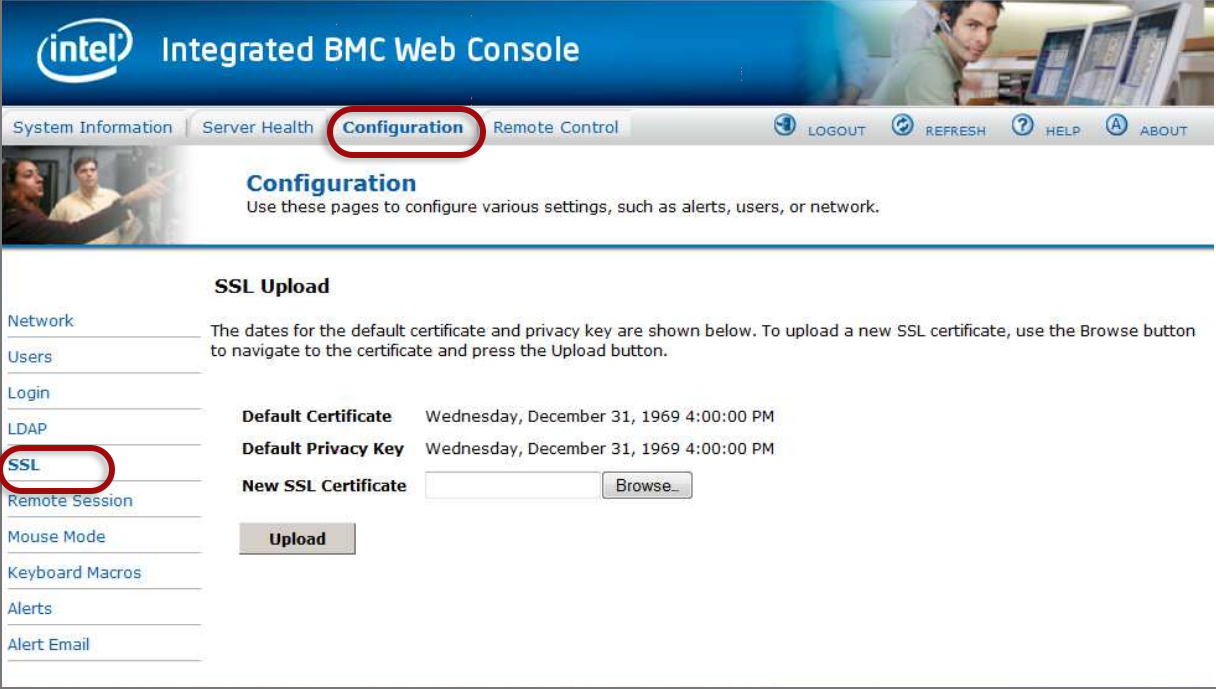
Upload an SSL certificate and privacy key, which allows the device to be accessed in a secure mode. On the Configuration tab, select SSL certification then browse and upload the SSL certificate and privacy key. 
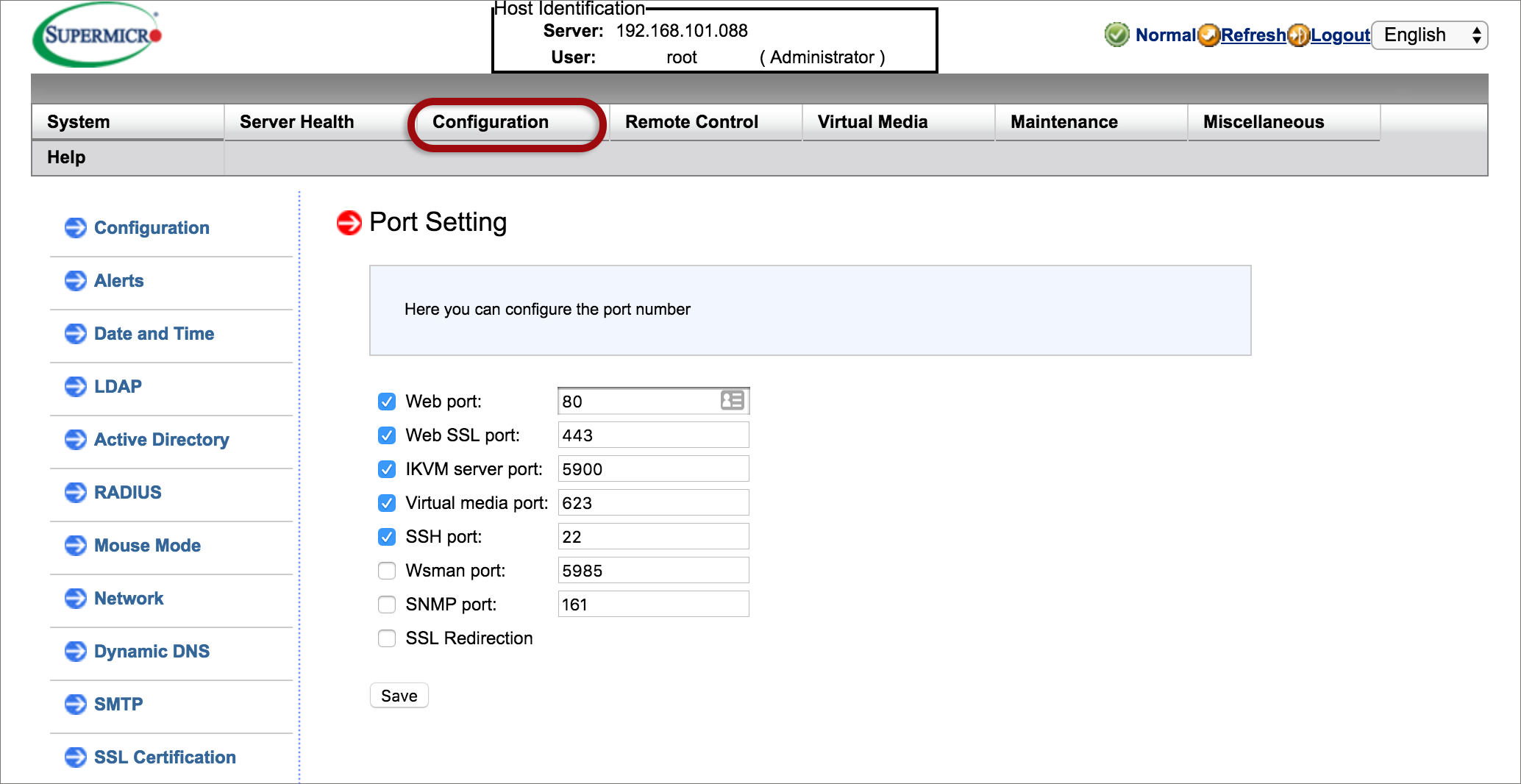
3. Block ports
On the Configuration tab, select Port from the left menu. The current or default ports will be displayed. You can change the default ports to those that are not commonly used to reduce the risk of malicious entry via these ports. Click Save.
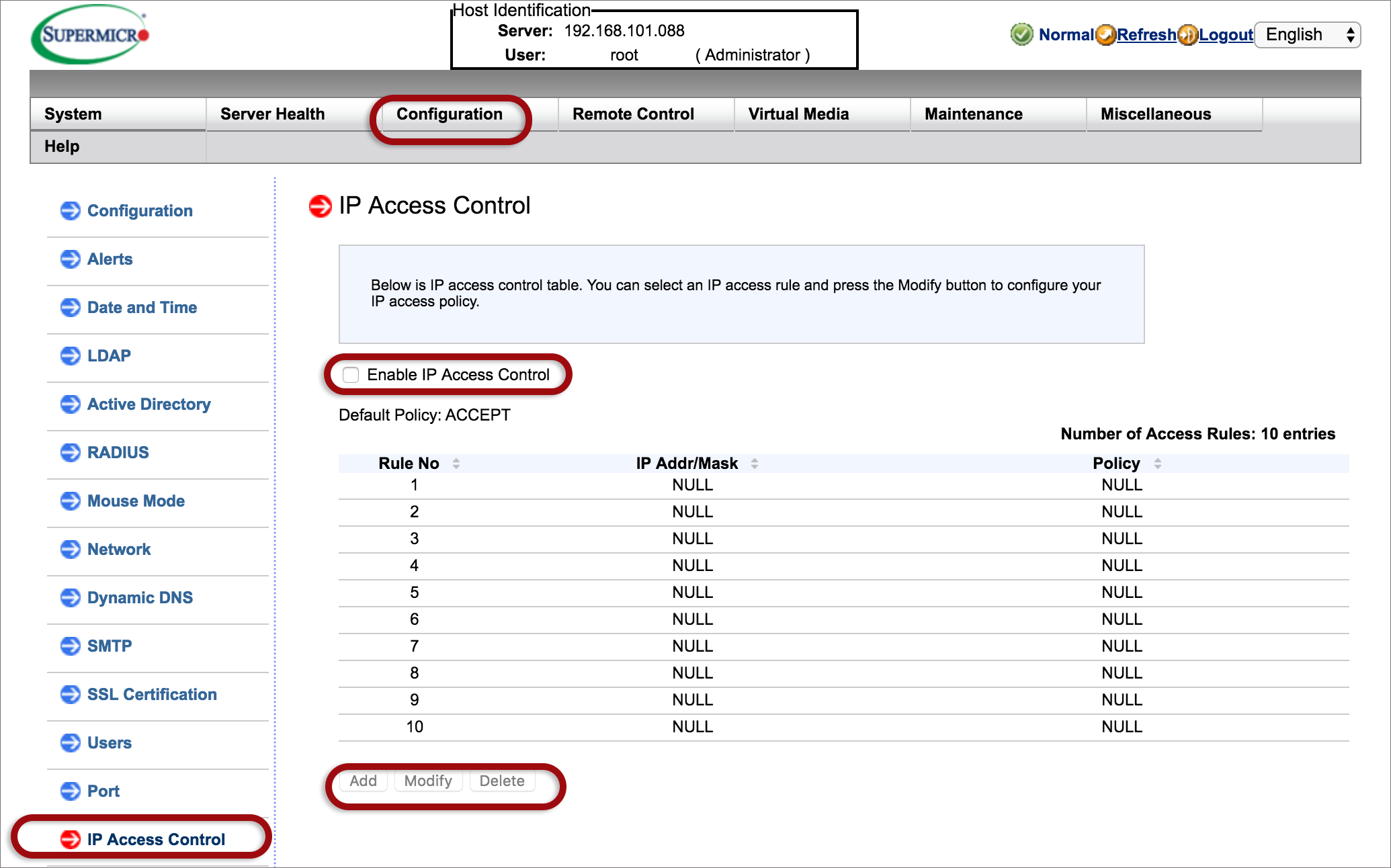
4. IP access control
For customers using a private IP address via the RMI Tunnel, this is not applicable. The network is only accessible as long as the bundle session is active.
This firewall feature allows you to limit access except from your IP(s) e.g. your office. Enabling the IP Access Control allows you to create IP Access rules.
- On the Configuration tab, select IP Access
- Tick to activate Enable IP Access Control
- Click Add to add your rule, providing your IP address.
- Enter the information needed
- IP Address/Mask: This item allows you to grant access to a specific IP address or a range of IP addresses. For example, if you wanted to specify a range of IP addresses from 192.168.0.1 to 192.168.0.126, you would enter 192.168.0.1/25.
- Policy: Select to allow access for the IP address(es) entered above. Select Drop to deny access.
- Click Save

5. Delete all services that are not used or required
If you don’t use certain services provided as options, e.g. mail, rather delete these services to avoid the risk of them being used for abuse.