How to fix the “Not Secure” website warning in Chrome
Does your website automatically open to the http version rather than https and displays the Not Secure message in the address bar?
We provide free Let’s Encrypt SSL/TLS certificates for all domains, which means that your website should be https compliant and shouldn’t be marked as “Not Secure”.
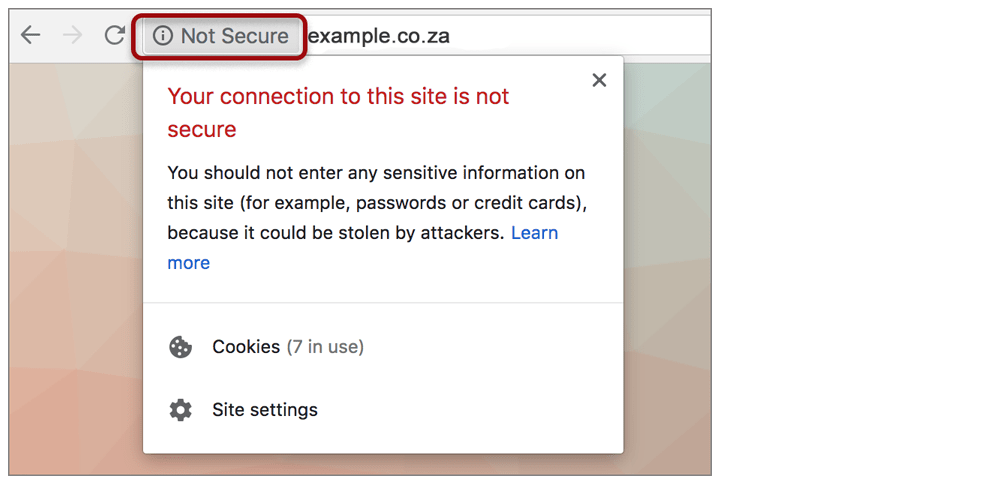
Since the release of Chrome 68 in July 2018, Google Chrome marks all http websites as “Not Secure”. When clicking on the ⓘ (info) icon , there is no reference to a certificate and the site is considered to not have an SSL/TLS certificate associated with the domain.
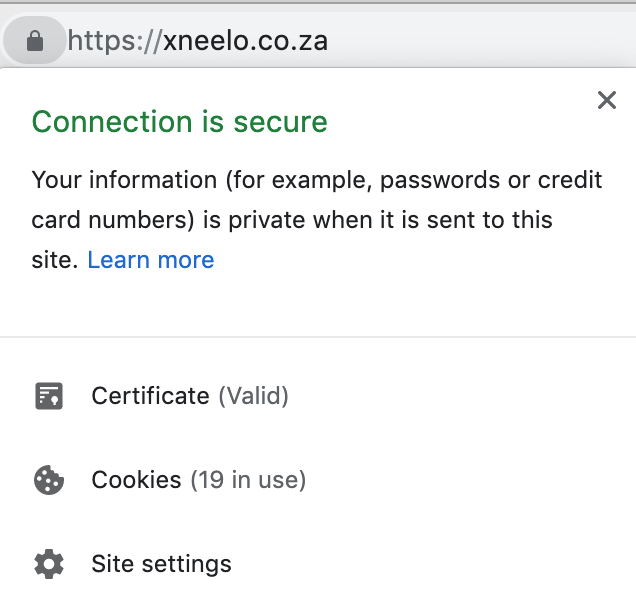
Chrome currently marks https-encrypted sites with a lock icon. When the lock icon is clicked, the information panel shows that a valid certificate is active.
http is the older protocol over which data is sent between your browser and the website server. https is the newer, secure version of http, whereby all communication between your browser and the website is encrypted.
This protocol is reliant on an SSL/TLS certificate.
Solution
You need to force HTTPS
As all domains hosted with us are provided with a free SSL certificate, your website should automatically open in https mode.
If your website automatically opens in the http version rather than https, you need to force https. Refer to the following articles for guidance:
- WordPress sites: Change your WordPress site to HTTPS
- Other sites: Force HTTPS using the .htaccess file (You can follow the step-by-step instructions even if you are unfamiliar with the .htaccess file)
Use the website WhyNoPadlock to assist you.
Further possible problems:
If you still get this error on some or all of your website pages after forcing HTTPS, check for the following:
1. Mixed content errors
This means that the page consists of a mix of HTTP and HTTPS content.
Websites that are updated to SSL, such as with Let’s Encrypt, move from using the http protocol to using https. However, if there is any content included in the page that specify http:// in their URL’s instead of https://, the browser will give a Mixed Content warning and may block the content. This content may be images, JavaScript, CSS or external resources like banners or advertising from external sites.
To fix this error, see: How to find and fix mixed content errors
2. Your site has no SSL/TLS
If your site doesn’t load securely even if you insert an https in front of the domain name in the browser, it may not have SSL activated. These are rare cases.
See Reasons why SSL/TLS may not work for your site to troubleshoot the problem.